AGM vs Lead Acid Battery Which Is Better For Your Needs

Featured image for which is better agm or lead acid battery
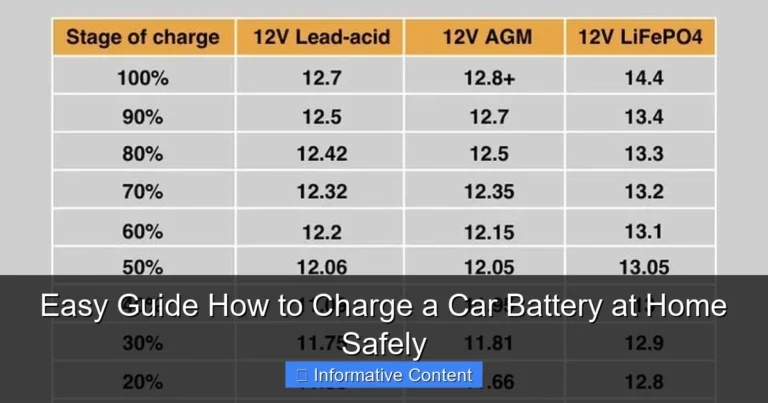
Image source: living.acg.aaa.com
Choosing between an AGM and a traditional lead-acid battery ultimately depends on your specific application and budget. AGM batteries offer superior performance, are maintenance-free, spill-proof, and boast a longer lifespan, making them ideal for demanding situations and deep-cycle uses. However, standard lead-acid options remain a highly cost-effective choice for less intensive power requirements, particularly where initial investment is a key concern.
Hey there, fellow adventurers and power seekers! Have you ever found yourself scratching your head, staring at a battery display, wondering which one is truly right for you? It’s a common dilemma. We all want reliable power. This could be for our RV, an off-grid cabin, or just ensuring our car starts every morning.
The world of batteries can be a bit confusing. Two types often come up: AGM and traditional lead acid batteries. Both have their fans. Both offer distinct advantages. But which one is the superior choice? Well, spoiler alert: there isn’t a single “best” option. It truly depends on your specific needs, budget, and how you plan to use it.
Today, we’re going to dive deep into these two powerhouses. We’ll explore their differences, pros, and cons. By the end, you’ll feel confident making an informed decision about the perfect battery for your unique situation. Let’s get charged up!
Key Takeaways
- Choose AGM: For maintenance-free operation and spill-proof safety.
- Select AGM: For deep cycling and superior vibration resistance.
- Opt for Lead Acid: To minimize upfront battery purchase costs.
- Consider Lead Acid: If regular water topping and ventilation are manageable.
- Prioritize AGM: For faster recharging and flexible mounting options.
- Match Battery Type: To your specific application’s demands and budget.
📑 Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics: What Are We Talking About?
Before we pick a winner, let’s understand our contenders. What exactly are AGM and lead acid batteries?
The Traditional Workhorse: Flooded Lead Acid Batteries
Imagine the battery under your car’s hood. Chances are, it’s a flooded lead acid battery. These batteries are the oldest and most common type. They use a liquid electrolyte solution. This is typically sulfuric acid and water. This solution creates electricity. The “flooded” part means the plates are submerged in this liquid.
They are reliable. They are often the cheapest upfront. But they are not sealed. This means they need regular maintenance. You often need to add distilled water. They can also spill acid if tipped. Proper ventilation is very important when charging. They can release hydrogen gas.
The Modern Upgrade: AGM Batteries
Now, let’s look at the Absorbent Glass Mat, or AGM, battery. This type is still a lead acid battery. But it has a clever design difference. The electrolyte is absorbed. It’s held in special fiberglass mats. These mats are packed tightly between the lead plates.
This design makes AGM batteries sealed and maintenance-free. You don’t need to add water. They also do not spill acid, even if broken. This makes them much safer to handle. They are often seen as a premium choice. Many people use them in RVs, boats, and off-grid setups. They offer many advantages. When considering an AGM vs lead acid battery, this sealed design is a key difference.
Key Differences: Performance and Practicality
Now that we know what they are, let’s get into the nitty-gritty. How do these two battery types truly compare in daily use?
Maintenance and Safety
This is where the first major split happens. Flooded lead acid batteries need upkeep. You must check water levels regularly. Top them off with distilled water, especially after deep discharges. They also vent gases during charging. This needs a well-ventilated space. They can spill corrosive acid if they tip.
AGM batteries are maintenance-free. Their sealed design means no water checks are needed. They are spill-proof. You can mount them in many positions. They produce very little gas. This makes them safer for indoor use. This ease of use is a huge plus.
Lifespan and Deep Cycling Capability
Flooded lead acid batteries last for around 200-500 charge cycles. This is if you avoid deep drains. Discharging below 50% shortens life. AGM batteries are tougher. They handle 400-800 cycles. Many can go deeper, to 80% discharge. This causes no major harm. This makes them excellent for off-grid or RV use. Regular deep cycling is common here. This longer cycle life often justifies their higher initial cost.
Charging Efficiency and Speed
AGM batteries charge faster. They lose less charge when idle (lower self-discharge). They accept higher charge currents. This leads to quicker recharges. This is an advantage if you have limited charging windows. Flooded batteries charge slower. They also lose charge faster when not in use. This difference is important for busy users. It is also key for solar power.
Temperature Tolerance
Traditional lead acid batteries perform well broadly. Extreme cold reduces capacity. Extreme heat shortens life. AGM batteries tolerate cold better. They show less capacity loss. They also handle vibrations well. This makes them great for vehicles. Both suffer from prolonged, very high heat.
Cost Consideration
Upfront cost is lower for flooded lead acid batteries. They are budget-friendly. This appeals if your budget is tight. Or if you need many batteries. Their ongoing maintenance is low (distilled water). AGM batteries cost more initially. Often 1.5 to 2 times more. But their longer life and no maintenance can save money. This happens over the long run. They also prevent damage from spills. When you weigh the AGM vs lead acid battery price, think long-term.
Applications: Where Each Battery Shines
So, now you know the differences. But how do you decide where each battery fits best? Let’s look at some real-world examples.
When Flooded Lead Acid Batteries Are a Great Choice
- Budget-Conscious Projects: If initial cost is your key concern.
- Stationary Backup Power: For fixed systems like sump pumps or small home backups.
- Utility Vehicles & Equipment: For vehicles with maintenance staff and less harsh conditions.
- Well-Ventilated Spaces: Garages or outdoor sheds with good airflow.
When AGM Batteries Are Your Best Bet
- RVs and Marine Applications: They are sealed, spill-proof, and vibration resistant.
- Off-Grid Living & Solar Systems: For daily deep cycling and faster charging.
- Sensitive Electronics & Indoor Use: They produce little gas and are spill-proof.
- High-Vibration Environments: Their robust build handles shocks well.
- Maintenance-Free Preference: If you want a “set it and forget it” power solution.
Consider your usage environment carefully. This will help you choose the right AGM vs lead acid battery.
Data Snapshot: A Quick Comparison
To make things even clearer, here’s a quick overview of how these two types stack up. Remember, these are general guidelines. Specific models can vary.
- Upfront Cost:
- Flooded Lead Acid: Low
- AGM: Moderate to High
- Maintenance:
- Flooded Lead Acid: Regular (water checks)
- AGM: Virtually none
- Deep Cycling:
- Flooded Lead Acid: Poor (dislike deep discharge)
- AGM: Good (handle deep discharge well)
- Lifespan (Cycles):
- Flooded Lead Acid: 200-500 cycles (50% DoD)
- AGM: 400-800 cycles (50% DoD, some deeper)
- Charging Speed:
- Flooded Lead Acid: Slower
- AGM: Faster
- Spill-Proof:
- Flooded Lead Acid: No
- AGM: Yes
- Vibration Resistance:
- Flooded Lead Acid: Low to moderate
- AGM: High
- Mounting Flexibility:
- Flooded Lead Acid: Upright only
- AGM: Multi-position (within limits)
Installation and Care Tips for Both Types
No matter which battery you choose, proper care extends its life. Here are some quick tips.
Always Use the Right Charger
This is crucial. Each battery type needs specific charging. Using the wrong charger damages it. Invest in a smart charger. It should have modes for both types. This ensures optimal charging. It keeps your battery healthy.
Ensure Proper Ventilation (Especially for Flooded Batteries)
For flooded batteries, ventilation is crucial. Install them in a well-aired space. This prevents gas buildup. AGM batteries need less. But good airflow helps prevent overheating.
Avoid Extreme Discharges and Overcharging
Avoid fully draining batteries. Especially flooded types. Recharge before 50% capacity. Overcharging is also bad. It causes gassing and corrosion. A good charge controller helps. It extends battery life.
Regularly Inspect Your Batteries
For flooded, check fluid often. Keep terminals clean and tight for both. Corrosion hurts performance. Visual checks catch issues early. This saves you trouble later. Good care of your AGM vs lead acid battery ensures long service.
Conclusion
Phew! We’ve covered a lot about AGM and lead acid batteries. It’s clear that both are fantastic power sources. But they shine in different scenarios.
Remember, the “better” battery isn’t a universal truth. It’s about finding the best fit for your unique setup. Consider your budget. Think about your application. How much maintenance are you willing to do? Will your battery face vibrations or extreme temperatures? Answering these questions will guide your choice.
If you need a reliable, low-cost option for a stationary setup, a flooded lead acid battery could be perfect. However, if you crave maintenance-free power, deep cycle capability, and durability for your RV or off-grid adventure, an AGM battery might be worth the extra investment.
Ultimately, whether you pick an AGM or lead acid battery, you’re making an informed decision. You’re choosing the right power solution for your needs. So go forth, power up, and enjoy the journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which is better overall, AGM or traditional lead-acid batteries?
It depends on your specific needs and priorities. While AGM batteries generally offer superior performance, longer life, and less maintenance, traditional flooded lead-acid batteries are often more budget-friendly upfront. Your ideal choice hinges on factors like application, budget, and desired longevity.
Are AGM batteries more expensive than lead-acid batteries?
Yes, AGM batteries typically have a higher upfront cost compared to conventional flooded lead-acid batteries. However, their increased lifespan, better performance, and reduced maintenance can sometimes lead to lower overall costs in the long run.
What are the main maintenance differences between AGM and lead-acid batteries?
A significant advantage of AGM batteries is that they are virtually maintenance-free, requiring no water top-offs because the electrolyte is absorbed in glass mats. Traditional flooded lead-acid batteries, conversely, need regular checks of electrolyte levels and distilled water replenishment to ensure proper function and lifespan.
Which battery type, AGM or lead-acid, offers a longer lifespan?
Generally, AGM batteries tend to have a longer cycle life and overall lifespan than standard flooded lead-acid batteries, especially when properly maintained and not deeply discharged. Their robust construction also makes them more resistant to vibrations and spills, contributing to their durability.
For deep cycle applications like RVs or marine use, is AGM or lead acid better?
For deep cycle applications, AGM batteries often outperform traditional flooded lead-acid options. They can handle deeper discharges without significant damage and recharge faster, making them an excellent choice for RVs, marine vessels, or off-grid systems where sustained power draw is common.
Do AGM batteries charge differently or perform better in certain conditions compared to lead-acid?
AGM batteries generally have a lower internal resistance, allowing them to charge much faster than conventional lead-acid batteries. They also perform better in extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, and are more resistant to vibration, making them suitable for demanding environments and versatile power needs.