How to Use Smart Battery Charger: A Simple Guide
Figuring out how to use smart battery charger can seem tricky at first. It’s common to feel unsure about these chargers because they have many features. Don’t worry, though! This guide breaks everything down in a way that’s easy to grasp. We’ll explore step by step what these chargers do, how they work, and how to use them safely. Get ready to become a smart charger expert!
What Is a Smart Battery Charger and How Does It Work?
A smart battery charger is a device that charges batteries but does much more than a basic charger. Regular chargers just pump electricity into a battery until it’s full. Smart chargers, however, use microprocessors to monitor and control the charging process. This means they can detect the battery’s condition, adjust the charging current and voltage, and prevent overcharging or damage. This helps extend the life of your batteries and keeps them working at their best.
Inside the Smart Charger
The core of a smart charger is its built-in intelligence. A microprocessor is like the brain of the device, analyzing information from sensors that monitor the battery’s voltage, current, and temperature. This information allows the charger to make smart decisions. For example, if the battery is very low, the charger might start with a higher current to charge it quickly. As the battery gets fuller, the charger will decrease the current to prevent overcharging. Smart chargers also have safety features to protect both the battery and the charger itself.
- Microprocessor Control: The key component is the microprocessor. This tiny computer reads data from the battery and adjusts the charging process accordingly. It constantly monitors voltage, current, and temperature, making real-time adjustments for optimal charging. This is what sets a smart charger apart from a basic charger.
- Multiple Charging Stages: Smart chargers often use several charging stages. The first stage, bulk charging, delivers a high current to quickly charge the battery. When the battery reaches a certain voltage, the charger switches to absorption mode, where it maintains a constant voltage. Finally, in float mode, the charger provides a small current to maintain the battery’s charge and prevent self-discharge.
- Built-in Safety Features: Smart chargers come with a variety of safety features, such as overcharge protection, short-circuit protection, and reverse polarity protection. These features prevent damage to the battery and the charger, as well as protect the user from potential hazards. Safety is a primary concern in the design of these chargers.
The microprocessor, often a System on a Chip (SoC), uses complex algorithms to manage the charging cycle. It can switch between different charging phases, like bulk charging, absorption, and float mode, to ensure the battery receives the precise amount of electricity it needs. The charging algorithms are designed to maximize the lifespan of various battery types, from lead-acid to lithium-ion.
These stages are crucial for battery health. The bulk stage quickly replenishes the energy, while absorption ensures the battery is fully charged without overcharging. The float stage keeps the battery topped off without damaging it. Different battery types may require slightly different charging stages, but the overall principle remains the same: a controlled and optimized charging process.
These safety mechanisms are critical. Overcharge protection stops the charging process when the battery is full, preventing damage. Short-circuit protection cuts off the current flow if the charger detects a short circuit, preventing fires and other hazards. Reverse polarity protection ensures that if the battery cables are connected incorrectly, the charger will not operate, protecting the charger and the battery from damage.
Choosing the Right Smart Battery Charger for Your Needs
Selecting a smart battery charger isn’t a one-size-fits-all situation. The right charger depends on the type of battery you need to charge and its capacity, the voltage, and the charging needs. Before purchasing a charger, you need to consider what you’ll be charging – a car battery, a motorcycle battery, or something else entirely? Different batteries require different charging currents and voltages, so matching the charger to the battery is essential for optimal performance and safety.
Battery Type and Compatibility
One of the first steps in picking a smart charger is identifying the battery type. Common battery types include lead-acid, lithium-ion, AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat), and gel batteries. Each type requires a specific charging profile. Using the wrong charger can damage the battery, reduce its lifespan, or even create a safety hazard. Always check the battery’s label or the manufacturer’s specifications to determine the correct charger.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: These are common in cars, boats, and other vehicles. Smart chargers for lead-acid batteries typically have three charging stages: bulk, absorption, and float.
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: These are used in many devices, including smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Lithium-ion chargers require precise voltage and current control to prevent damage.
- AGM and Gel Batteries: These are types of lead-acid batteries. AGM batteries are often used in motorcycles and ATVs, while gel batteries are used in applications that require deep cycling. These batteries require specific charging profiles to maintain their health.
Lead-acid batteries are widely used because they are relatively inexpensive and reliable. The bulk stage quickly charges the battery, the absorption stage ensures it’s fully charged, and the float stage maintains its charge. Smart chargers designed for lead-acid batteries often have a desulfation mode, which can help to revive batteries that have been sitting unused for a long time.
Lithium-ion batteries have become increasingly popular because they are lightweight, have a high energy density, and can be recharged many times. They are more sensitive to overcharging and over-discharging than lead-acid batteries, so smart chargers designed for lithium-ion batteries often have advanced protection features. These chargers typically use a constant-current, constant-voltage (CC/CV) charging method.
AGM and gel batteries are designed for different uses. AGM batteries are known for their ability to handle vibrations and provide high starting power, while gel batteries are known for their ability to withstand deep discharges. Both AGM and gel batteries can be damaged by improper charging, so it’s critical to use a charger that’s designed for these battery types. These smart chargers often have specific settings that will work to charge each battery safely.
Voltage, Current, and Capacity
You also need to understand the voltage, current, and capacity of the battery. The voltage of the charger should match the battery’s voltage (e.g., 12V, 24V). The charging current (measured in amps, A) should be appropriate for the battery’s capacity (measured in amp-hours, Ah). A general rule is to charge at a current that’s about 10% of the battery’s capacity. For example, a 100Ah battery would ideally be charged at 10A.
- Voltage Matching: Make sure the charger’s output voltage matches the battery’s voltage. Using a charger with the wrong voltage can damage the battery or prevent it from charging properly.
- Current Considerations: The charging current is the speed at which the battery charges. A higher current will charge the battery faster, but it’s important not to exceed the battery’s recommended charging current.
- Capacity and Charging Time: The battery’s capacity determines how much energy it can store. The charger’s current and the battery’s capacity determine how long it takes to charge.
Most common batteries are 12V, but some systems use 24V or higher. Always check the battery’s specifications to ensure compatibility. Using a 6V charger on a 12V battery won’t work, and using a 24V charger on a 12V battery will damage it.
Charging at too high a current can overheat the battery, reducing its lifespan and potentially causing a hazard. A good rule of thumb is to charge at around 10% of the battery’s capacity in amp-hours. So, a 100Ah battery would ideally be charged at 10A.
A larger capacity battery will take longer to charge than a smaller one, assuming the same charging current. For example, a 100Ah battery charged at 10A will take approximately 10 hours to charge from empty, but this will vary depending on the charger’s efficiency and the battery’s condition.
How to Safely Use a Smart Battery Charger: Step-by-Step
Safety is the most important factor when using a smart battery charger. Following the correct procedures will ensure that you protect the battery, the charger, and yourself. This step-by-step guide is designed to make the process easy and keep you safe. Always read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions before using any smart battery charger.
Connecting the Charger
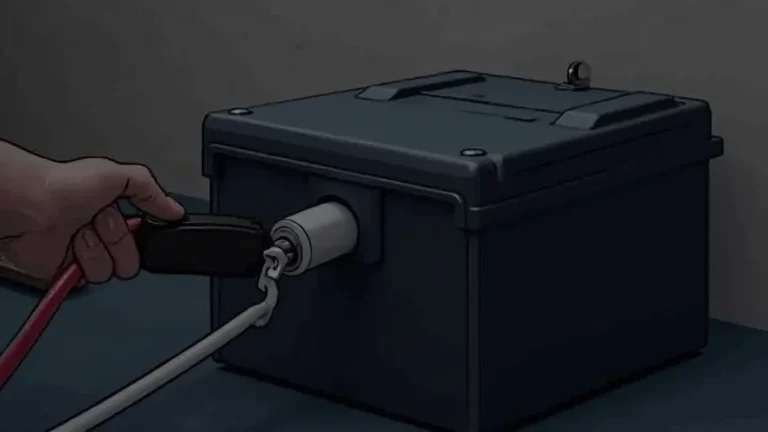
Connecting the smart battery charger correctly is essential for safety and effective charging. Start by ensuring the charger is turned off before making any connections. The standard process involves connecting the charger to the battery terminals in the correct order to prevent sparks and damage. Double-check that the connections are secure to provide good contact and effective charging.
- Power Off: Turn off the charger and disconnect it from the power outlet. This minimizes the risk of electrical shock and potential damage during the connection process.
- Connect the Positive Cable: Connect the red (+) positive cable from the charger to the positive (+) terminal of the battery. Ensure a firm, secure connection.
- Connect the Negative Cable: Connect the black (-) negative cable from the charger to the negative (-) terminal of the battery, or to a grounded chassis point if recommended by the manufacturer.
- Plug in the Charger: Once the cables are securely connected, plug the charger into a power outlet.
- Select the Charge Mode (If Applicable): Some smart chargers have settings for different battery types. If your charger has this option, select the correct mode for your battery.
Always start by turning off and unplugging the charger. This is a crucial first step for safety, because it eliminates the risk of accidental electrical shock or damage to the equipment or battery.
The positive terminal is usually marked with a “+” symbol or is red in color. Connecting the cables in the correct order minimizes the risk of short circuits and ensures that the battery charges properly. A good, tight connection is vital for the safe and efficient transfer of electricity.
The negative terminal is typically marked with a “-” symbol or is black in color. Connecting the negative cable last helps prevent sparks, especially if the positive cable accidentally touches the chassis. Ensuring a clean and secure connection is crucial for the charging process.
Plugging in the charger completes the circuit. At this point, the charger should turn on and begin its diagnostic process. If the connections are correct and the charger detects a valid battery, it will start charging.
Many smart chargers are designed to charge various battery types, like lead-acid, AGM, and lithium-ion. Selecting the right mode will ensure the battery receives the proper charging profile, protecting it from damage and maximizing its lifespan. This will ensure the charger applies the right voltage and current levels for your specific battery type.
Monitoring the Charging Process
Even though smart chargers are designed to handle the charging process automatically, it’s good practice to keep an eye on things. This can help you identify any problems early on. A well-placed look can also reassure you that the charging process is proceeding normally. Pay attention to the charger’s display and any indicators that it provides, as these offer valuable insight.
- Check the Display: Most smart chargers have a display that shows the charging progress, voltage, current, and sometimes the battery’s state of charge.
- Monitor for Unusual Behavior: Watch for any unusual signs, such as excessive heat, hissing sounds, or bulging of the battery casing. If you observe any of these, immediately disconnect the charger and seek assistance.
- Charging Time: Although smart chargers adjust the charging process, they still take time to fully charge a battery. The charging time depends on the battery’s capacity and the charger’s current output.
- Full Charge Indication: The smart charger will typically indicate when the battery is fully charged. This could be a light turning green, a message on the display, or the charger automatically switching to float mode.
The display is your primary source of information during the charging process. It gives you real-time data on how the battery is charging and what stage the charger is in. Pay attention to any error messages or warnings that may appear.
Although rare, problems can happen. Excessive heat can be a sign of overcharging or a fault in the battery. Hissing sounds can indicate a gas leak, and a bulging battery can be a sign of internal damage. Do not ignore unusual signs; take immediate action.
Charging a battery can take anywhere from a few hours to a full day, depending on the factors. Check the charger’s manual for estimated charging times and plan accordingly. Over-the-course-of-time, it will be easier to gauge how long your battery needs to fully charge.
The notification that the charging is complete is the cue to disconnect the charger. It’s often indicated by a visual or audible signal. When the charge is complete, the charger will switch to a maintenance or float mode to maintain the battery’s charge. Now you can remove the charger without worry.
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
While smart battery chargers are very reliable, you may encounter issues. Knowing how to diagnose and address these problems can save you time and potential frustration. Most issues are typically simple to resolve and relate to connectivity, battery condition, or charger settings. If the charger displays an error message or the battery fails to charge, troubleshoot it to identify and resolve the issue.
Charger Not Turning On
If the charger doesn’t turn on, the first thing to check is the power source. This is something often missed. After checking the power source, make sure the charger’s internal fuse is not blown and that the power cord is in good condition. If the charger does not receive power, it will not operate. Simple steps can often resolve this kind of problem.
- Check the Power Outlet: Ensure the charger is plugged into a working power outlet. Try plugging another device into the same outlet to confirm it’s functioning.
- Inspect the Power Cord: Examine the power cord for any damage, such as cuts or frayed wires. Replace the power cord if necessary.
- Check the Fuse: Some smart chargers have an internal fuse that protects the charger from overloads. Check the fuse and replace it if it’s blown.
- Factory Reset: Many smart chargers can be reset to their factory settings. Refer to the owner’s manual to see if a reset is possible and, if so, how to perform it.
A simple yet common issue is a faulty power outlet. Before assuming the charger is broken, check the outlet by plugging in a lamp, a phone charger, or another device. If that device works, the outlet is fine; if not, you may need a different outlet.
The power cord is the pathway to the outlet, and any damage can prevent the charger from working. Visible damage like cuts, abrasions, or exposed wires require immediate attention. Using a damaged cord can be a hazard, so replace it immediately if you see any issue.
Internal fuses safeguard the charger from electrical surges or overloads. Consult the owner’s manual for the fuse’s location and proper replacement instructions. Using the wrong fuse can damage the charger and can pose a risk.
Performing a reset can clear any settings that might be interfering with the charger’s operation. This process will reset any programming to defaults, which may resolve some of the more complex issues. Follow the manual to avoid any damage to the charger.
Battery Not Charging
If the battery doesn’t charge, the problem could be a bad connection, an issue with the battery itself, or improper charger settings. Often, the solution is as simple as checking the connections or selecting the correct charge mode. Thorough checks and following diagnostic steps can help resolve the problem. If a battery does not charge, several factors can cause this, and identifying the cause is the first step in solving the problem.
- Check the Connections: Make sure the charger cables are securely connected to the battery terminals. Clean the terminals if necessary to ensure good contact.
- Confirm the Charge Mode: Ensure the charger is set to the correct mode for your battery type. Using the wrong mode can prevent the battery from charging properly.
- Battery Condition: The battery may be damaged or sulfated. A smart charger may not be able to charge a severely damaged battery. Consider testing the battery with a multimeter or having it professionally tested.
- Try a Different Charger: If possible, test the battery with another smart charger to see if the issue is with the battery or the original charger.
The most common issue with a battery not charging is a bad connection. If the connections are loose or the terminals are corroded, the electricity will not flow effectively. It is vital to ensure that the connections are tight and the terminals are clean.
Different battery types require specific charging profiles. If you have the wrong mode, the charger may not deliver the right voltage or current, or it may not recognize the battery. Always refer to the battery’s specifications and the charger’s manual.
If the battery is old, damaged, or has been left discharged for an extended period, it may not accept a charge. Testing the battery’s voltage and capacity can help determine if it is still usable. If the battery is severely sulfated, it may require specialized charging or replacement.
If the battery charges with another charger, the original charger may be faulty. If the battery does not charge with another charger, the problem is more likely with the battery itself. This will provide some clarity on the problem.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Can I leave the smart battery charger connected overnight?
Answer: Yes, in most cases, you can leave a smart battery charger connected overnight. Smart chargers are designed to stop charging when the battery is full and switch to a maintenance mode, preventing overcharging and damage. However, always check the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific charger model.
Question: Will a smart charger work on a completely dead battery?
Answer: It depends on the charger and the condition of the battery. Some smart chargers have a recovery mode for deeply discharged batteries. If the battery is severely damaged or sulfated, the charger may not be able to revive it. Always consult the charger’s manual for specific instructions.
Question: Can I use a smart charger on a motorcycle battery?
Answer: Yes, you can use a smart charger on a motorcycle battery, provided the charger is compatible with the battery type (e.g., lead-acid, AGM, gel). Choose a charger with the appropriate voltage (12V) and a charging current suitable for the battery’s capacity.
Question: Are smart battery chargers safe to use?
Answer: Yes, smart battery chargers are generally safe because they incorporate multiple safety features, such as overcharge protection, short-circuit protection, and reverse polarity protection. However, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the charger correctly to ensure safe operation.
Question: How do I know when my battery is fully charged with a smart charger?
Answer: Most smart battery chargers indicate when the battery is fully charged through a display, an indicator light, or an audible signal. The charger will often switch to a maintenance or float mode after the battery is fully charged, ensuring it stays topped up without overcharging.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how to use smart battery charger is a key skill. These chargers are great at keeping your batteries in good shape. With a smart charger, you get more than just a quick charge. You get all sorts of special features that keep your batteries safe and sound. We’ve gone over the essential steps, from choosing the right charger and connecting it, to watching the process and solving any issues that come up. Remember to always match your charger to your battery type, and always follow safety first. Don’t be shy about consulting your charger’s manual – it’s your best resource! Now that you have explored the essentials, you are ready to keep your batteries charged and ready for action. Happy charging!