Is a Jump Starter Safe for Your Car’s Electronics?
Getting your car started with a jump starter can feel tricky, and a common question is is a jump starter safe for car electronics. It’s totally normal to worry about damaging the fancy computers in your car. Luckily, using a jump starter doesn’t have to be scary! We’ll explore how these devices work and how to use them the right way, so you can safely jump-start your car without any problems. Let’s get started and clear up any doubts!
How Jump Starters Work
Jump starters, also known as portable power stations, are like tiny batteries that pack a big punch. They store electricity and are designed to provide a burst of power to start a car with a dead battery. Think of it as a quick energy boost. These devices typically have clamps that connect to your car’s battery terminals. When connected, the jump starter sends power to your car’s electrical system, allowing the engine to start. They are a convenient alternative to asking someone for a jump or waiting for roadside assistance, providing an easy solution when you’re stuck.
Internal Components
A jump starter consists of several important parts. The core is the battery, often a lithium-ion or lead-acid type, which stores the electrical energy. Circuitry within the jump starter regulates the flow of electricity, preventing damage to the car’s electronics. Protection features include short circuit protection and reverse polarity protection. The exterior is usually a durable casing with clamps for connecting to the car battery. This design prioritizes safety, giving you peace of mind when you use the device.
- Battery: The power source is usually lithium-ion or lead-acid. These batteries are designed to hold and release large amounts of electricity quickly, which is necessary for starting a car engine. The capacity of the battery determines how many times it can jump-start a car before needing to be recharged. Higher capacity means more starting attempts.
- Circuitry: This is the brain of the jump starter. It manages the power flow to protect both the jump starter and your car’s electronics. It ensures the correct voltage and current are delivered, preventing any surges or other electrical issues that could cause damage.
- Clamps: Clamps attach to the car battery terminals. They are usually color-coded (red for positive and black for negative) to help you connect them correctly. Quality clamps ensure a good connection, which is important for delivering power efficiently.
- Safety Features: Most jump starters have built-in safeguards, such as protection against reverse polarity (connecting the clamps backward), overcharging, and short circuits. These features make jump starters safe to use and protect your car.
Voltage and Current Considerations
A jump starter’s voltage must match your car’s battery voltage to start your engine effectively. Most cars use a 12-volt system. The current, measured in amps, represents the power output. A higher current is necessary to turn over the engine, particularly in cold weather. It’s vital to check the specifications of both your car battery and the jump starter to ensure compatibility. This prevents both damage to your car and jump starter failure.
- Matching Voltage: Always check that the jump starter’s voltage matches your car battery’s voltage. This is usually 12 volts for standard vehicles. Using a jump starter with the incorrect voltage could lead to serious damage to your car’s electrical components.
- Current Rating: The current rating indicates how much power the jump starter can provide. It’s often measured in “peak amps” and “cranking amps.” Your jump starter should have a cranking amp rating at least equal to or slightly higher than your car battery’s requirement. This ensures it has enough power to start your engine.
- Reverse Polarity Protection: This function is key for protecting your car. It guards against damage by preventing the jump starter from operating if the clamps are connected to the battery incorrectly (positive to negative and vice versa).
- Short Circuit Protection: Prevents damage to the jump starter and your car if the clamps touch each other or cause a short circuit. It is vital for your safety.
Ensuring Safety: Connecting and Using a Jump Starter
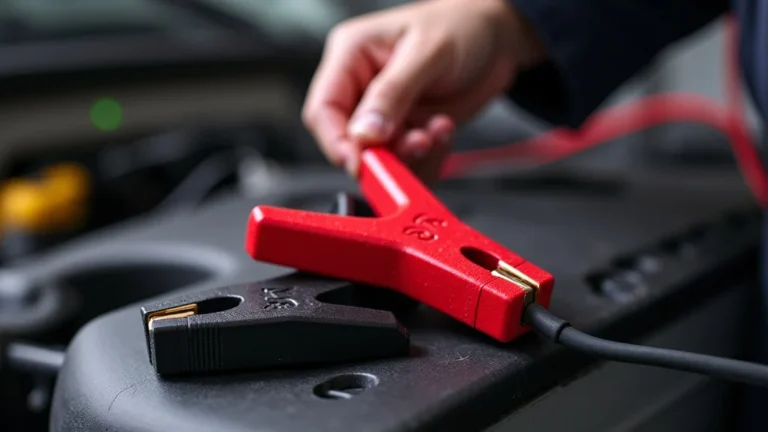
To safely use a jump starter, you need to follow the proper steps. Make sure the jump starter is turned off before connecting the clamps. Connect the red clamp to the positive (+) terminal of your car battery and then connect the black clamp to a grounded metal surface on your car, away from the battery. After connecting, turn on the jump starter and try to start your car. If your car starts, disconnect the clamps in the reverse order and let your car run for a while to recharge the battery.
Step-by-Step Guide for Safe Connection
The correct connection process is very important. Always start by turning off the jump starter and any electrical components in your car. This minimizes the risk of electrical surges. Connecting the clamps in the right order and to the proper terminals reduces the risk of sparks or damage to your car’s electronics. Following these instructions will allow you to do the jump safely.
- Turn Off Everything: Switch off your car’s ignition and all accessories (lights, radio, etc.). This step prevents electrical surges when you connect the jump starter.
- Locate Your Battery: Find your car battery. The battery is often under the hood, but sometimes it is located in the trunk or under a seat.
- Connect the Red Clamp: Attach the red (positive) clamp of the jump starter to the positive (+) terminal of your car battery. Make sure the clamp has a firm grip on the terminal.
- Connect the Black Clamp: Connect the black (negative) clamp to a bare metal surface on the car’s frame, away from the battery. This may be a bolt or a part of the engine block. Avoid connecting it to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Turn On the Jump Starter: Turn on the jump starter. Some models have an on/off switch or require you to press a button.
- Start Your Car: Try to start your car. If it doesn’t start right away, wait a few minutes and try again. Do not crank the engine for more than 5-10 seconds at a time.
- Disconnect the Clamps: Once the car is running, carefully remove the clamps in the reverse order of how you connected them. First, remove the black clamp from the car frame, then the black clamp from the jump starter. Finally, remove the red clamp from the jump starter, then from the car battery.
Important Precautions and Safety Tips
Always take precautions. Never smoke or have an open flame near the battery, because batteries can release explosive hydrogen gas. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from any sparks or acid. Keep the jump starter away from children and pets. If you are unsure about any part of the process, it is best to consult your car’s manual or ask a professional for help. Remember, safety first!
- Wear Eye Protection: Safety glasses protect your eyes from sparks, battery acid, and debris.
- Avoid Sparks and Flames: Never smoke or have open flames near the battery. Batteries can release hydrogen gas, which is very flammable.
- Check the Clamps: Inspect the clamps for corrosion or damage. Replace them if necessary. Poor clamps can cause a poor connection or sparks.
- Ventilation: Make sure you are working in a well-ventilated area to avoid the buildup of harmful gases.
- Read the Manual: Always read the instructions for both the jump starter and your car. This makes sure you are using the equipment safely.
Understanding Car Electronics and Risks
Modern vehicles are filled with sensitive electronic components, which control everything from the engine and transmission to the infotainment system and safety features. These components can be sensitive to voltage fluctuations, such as surges or spikes. Using a jump starter can introduce risks if not used correctly. Reverse polarity and improper connections are the main things to avoid. Following the correct procedure will reduce the risks.
Sensitive Electronic Components
Modern cars have many computer systems that control different functions. The engine control unit (ECU) manages the engine’s performance. The transmission control unit (TCU) manages gear changes. The antilock braking system (ABS) and the airbag control module (ACM) are responsible for safety. These components rely on a stable voltage supply to work correctly. A jump starter can affect these components if there is a voltage surge. The electronic components are connected to sensors and actuators. Any electrical problems could impact the safety of the vehicle.
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU manages the engine’s performance, including fuel injection, ignition timing, and emissions control. Damage to the ECU can cause engine malfunctions.
- Transmission Control Unit (TCU): The TCU manages gear changes, ensuring smooth and efficient operation of the transmission.
- Antilock Braking System (ABS) Module: The ABS prevents wheel lockup during braking. Damage to this system affects your car’s safety and braking performance.
- Airbag Control Module (ACM): The ACM controls the deployment of airbags in the event of a collision. Issues with this module can compromise passenger safety.
- Infotainment System: Modern cars often have advanced infotainment systems. Damage to these systems can lead to loss of functionality.
Potential Risks and How to Avoid Them
When using a jump starter, there are a few risks to keep in mind. One of the biggest is reverse polarity. If you connect the clamps backward, you could damage the car’s electronics. Another risk is a voltage surge. Always make sure the jump starter is off before connecting the clamps. This avoids any sudden power surges. Following the steps in this post will help you avoid these problems.
- Reverse Polarity: This is when you connect the positive clamp to the negative terminal, and vice versa. It can cause serious damage to your car’s electronics. Most modern jump starters have reverse polarity protection.
- Voltage Surges: These can occur if the jump starter malfunctions or if the connection is not made correctly. This can damage sensitive components.
- Overcharging: Overcharging can occur if the jump starter provides excessive voltage. This is uncommon with modern jump starters that have voltage regulation.
- Using the Incorrect Jump Starter: Always use a jump starter with the correct voltage and current rating for your car. Using one that’s too weak can lead to problems.
- Failure to Follow Instructions: Not following the manufacturer’s instructions for the jump starter can lead to damage. Always follow the steps carefully.
Choosing the Right Jump Starter for Your Car
The right jump starter for your car depends on its size and the type of engine. It’s best to choose one with sufficient power to start your car. Consider the portability, features, and safety measures. A jump starter with built-in protection and easy-to-use controls will make jump-starting your car easier. Look for one with extra features, such as USB ports for charging your devices. You will want something that meets your needs.
Factors to Consider When Purchasing
Several factors will guide your purchasing decision. Consider the peak amps, as this will impact your car’s ability to start in cold conditions. The battery capacity determines the number of starts you can get before recharging. The size and weight are important if you want a portable device. Look for extra features that suit your lifestyle. Weigh these factors to find the best jump starter.
- Peak Amps: Choose a jump starter with a high peak amp rating. It should be at least equal to, or higher than, the recommended starting amps for your car.
- Battery Capacity: Larger battery capacity means more jump-start attempts. Consider how frequently you’ll need the jump starter.
- Portability: Look for a compact and lightweight jump starter if you need one that is easy to store and carry.
- Safety Features: Make sure the jump starter has protection against reverse polarity, overcharge, and short circuits.
- Additional Features: Many jump starters have USB ports for charging phones and other devices. Some even include built-in flashlights.
Top Jump Starter Brands and Models
There are many jump starter brands. Brands like NOCO, Clore Automotive, and Schumacher are well-known for producing high-quality and reliable jump starters. Research different models and read reviews to ensure you find one that fits your needs. Compare their features, power ratings, and customer reviews to make an informed choice. It helps to check online reviews before you buy.
| Brand | Model Example | Key Features | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|
| NOCO | GB70 | High peak amps, reverse polarity protection, integrated flashlight | Cars, trucks, SUVs |
| Clore Automotive | Jump-N-Carry JNC660 | High cranking power, durable design, heavy-duty clamps | Commercial vehicles, heavy-duty applications |
| Schumacher | SL1316 | Compact, portable, USB charging | Cars, light trucks |
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Can I damage my car’s electronics using a jump starter?
Answer: If used correctly, jump starters are safe for your car’s electronics. Follow the correct connection procedure and ensure the jump starter has the necessary safety features like reverse polarity protection.
Question: What should I do if my car doesn’t start after using a jump starter?
Answer: If your car doesn’t start, double-check the connections and make sure the jump starter is fully charged. You may also need to test the battery and other electrical systems, because there might be other issues.
Question: Are all jump starters safe for all cars?
Answer: Not all jump starters are suitable for all cars. Make sure the jump starter has enough power for your car. Check the voltage and peak amps to make sure it matches your vehicle’s requirements.
Question: How often should I recharge my jump starter?
Answer: You should recharge your jump starter after each use and at least every three to six months to maintain its battery capacity. Check the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Question: Can I use a jump starter in extreme temperatures?
Answer: Most jump starters can function in a wide range of temperatures, but performance may be affected in extreme cold. Check the manufacturer’s specifications for temperature ranges.
Final Thoughts
So, is a jump starter safe for car electronics? Yes, it absolutely can be! You can safely use a jump starter by following the correct steps and understanding its components. By choosing the right jump starter with safety features and following the proper connection procedure, you can protect your car’s sensitive electronics. Remember to prioritize safety by avoiding sparks, making sure the connections are correct, and making sure the jump starter is off while connecting. This will help you get your car started quickly and safely when you need it. By using a jump starter the right way, you are ready for a dead battery, giving you some peace of mind on the road!