How to Connect Charger Clamps Safely For Battery Charging
Figuring out how to connect charger clamps safely can seem tricky, especially if you’re new to car maintenance. It’s a common area where people get confused, as getting it wrong can lead to sparks or even damage. Don’t worry, though! It’s much easier than you might think. We’ll break down the process step-by-step, making sure you know exactly what to do. Prepare to become a battery-charging pro by following along.
Prepare Your Battery Charging Station
Before you even think about grabbing those charger clamps, some prep work is needed. This initial stage ensures your safety and the longevity of your battery. It’s about more than just grabbing a charger and hoping for the best. A little time spent here pays off in the long run. We’re talking about clearing the area, examining your battery, and ensuring you have the right equipment ready to go. Consider this the foundation for a safe and effective charging session.
Safety First: Gather Your Equipment
First off, locate a well-ventilated space. Car batteries, especially when charging, can release hydrogen gas, which is highly flammable. Avoid charging in enclosed spaces like garages without good airflow. A garage door left partially open provides ventilation. Wear safety glasses to protect your eyes from any potential sparks or acid splashes. Also, it’s a good idea to wear gloves to protect your hands. Ensure that your charger is compatible with your battery type (e.g., lead-acid, AGM, or lithium-ion). Different battery types require different charging settings.
- Safety Glasses: Crucial to protect your eyes from battery acid or any debris.
- Gloves: Protect your hands from contact with acid and dirt.
- A Car Battery Charger: Ensure the charger is rated for your battery’s voltage (e.g., 12V or 24V).
- Ventilated Area: Charge batteries in a well-ventilated spot to disperse potentially explosive gases.
- Clean Cloth: Wipe down the battery terminals to remove corrosion.
Selecting the right equipment is a basic, yet vital, first step. Chargers come in a variety of types, from basic trickle chargers to smart chargers that monitor the battery’s condition. The right charger will prevent overcharging and damage to the battery. Using the wrong charger can severely shorten its lifespan or, in worst-case scenarios, pose a fire hazard. Always review the charger manual.
Battery Inspection and Cleaning
Inspect your battery before you begin the charging process. Look for any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or swelling. If you see any of these, the battery might be compromised and needs
- Check the Battery Case: Look for cracks, bulges, or leaks.
- Clean Terminals: Remove any corrosion with a baking soda and water solution.
- Inspect Cables: Check the cables for damage.
- Ensure the Battery Is Secure: Make sure the battery is held steady to avoid any movement during the process.
Battery corrosion is the buildup of sulfate crystals on the terminals, caused by the release of hydrogen gas and acid vapors. This can obstruct the flow of electricity, making it difficult for the vehicle to start. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the battery terminals can significantly improve the vehicle’s performance and prevent starting troubles. The presence of corrosion often suggests a charging issue, such as overcharging.
The Right Way to Connect Charger Clamps
Now, let’s explore the critical steps for correctly attaching those charger clamps. Misconnecting the clamps can cause sparks and damage the battery or charger. These steps are a core skill for any vehicle owner. Following them closely guarantees a safe and productive charging experience. This section is all about getting the connections right the first time.
Understanding Polarity: Positive and Negative
Car batteries have two terminals: positive (+) and negative (-). The positive terminal is usually marked with a “+” symbol or a red cap, while the negative terminal is marked with a “-” symbol or a black cap. The charger clamps also have a positive and a negative clamp, usually marked with red and black colors respectively. It’s crucial to connect the clamps to the correct terminals. Connecting them backward can damage the battery, the charger, or even the car’s electrical system. This fundamental concept is central to the safety and success of the charging process.
- Positive (Red) to Positive (+): Connect the red clamp to the positive terminal of the battery.
- Negative (Black) to Negative (-): Connect the black clamp to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Double-Check the Connections: Always verify that you’ve connected the clamps correctly before turning on the charger.
- Avoid Touching the Clamps Together: Never let the clamps touch each other when they’re connected to the battery or charger.
The correct polarity is essential for the flow of electric current. Current flows from the positive terminal, through the car’s electrical system, and back to the battery’s negative terminal. Reversing this flow can cause severe problems. For instance, the alternator, which charges the battery while the car is running, is designed to operate with correct polarity, and it will be damaged if connected backward. A blown fuse or electrical component can be another outcome of improper connections.
Step-by-Step Clamping Procedure
The sequence for connecting the charger clamps is very important. Always connect the positive (red) clamp first, then the negative (black) clamp. This order minimizes the risk of a short circuit if the positive clamp accidentally touches any metal part of the car’s chassis. Once you’ve attached the clamps to the battery terminals, make sure they are secure. Loose clamps can cause arcing and heat, potentially leading to a fire. This precise sequence is an important safety consideration.
- Connect the Positive Clamp: Attach the red (positive) clamp to the positive (+) terminal of the battery.
- Connect the Negative Clamp: Attach the black (negative) clamp to the negative (-) terminal or a metal chassis part away from the battery.
- Turn On the Charger: Plug in the charger and turn it on, following the charger’s instructions.
- Monitor the Charging Process: Keep an eye on the charger’s display for progress.
- Disconnect in Reverse Order: Turn off the charger, then disconnect the negative clamp first and finally the positive clamp.
Many modern chargers have safety features that can detect incorrect connections or short circuits, turning off automatically to prevent damage. However, it’s still very important to follow the correct procedure. Using a charger with these features offers an extra layer of protection, but good practices are the best starting point. The charger’s display will tell you the voltage and charging rate, allowing you to gauge the battery’s condition.
Safe Charging Practices and Precautions
Charging a car battery involves safety steps beyond just connecting the clamps. Leaving the charger unattended for extended times or using the wrong settings can be harmful. The aim is to charge the battery efficiently without overdoing it. Remember, overcharging can lead to battery damage and potential hazards. Careful supervision and adherence to manufacturer instructions are key to a secure and efficient charging session. Your diligent approach plays a vital role in ensuring a good outcome.
- Do Not Overcharge: Follow the charger’s instructions for the correct charging time and amperage.
- Monitor the Battery: Check the battery for heat or swelling during the charging process.
- Use the Correct Settings: Select the right charging voltage and amperage for your battery type.
- Ventilate the Area: Make sure the charging area is well ventilated to prevent the build-up of flammable gases.
Overcharging a battery generates excess heat and can cause the electrolyte to boil, leading to battery damage. This heat can also cause the battery to swell or even explode. Using the wrong settings, such as a higher amperage than recommended, can also speed up the process to damage. Many chargers are equipped with automatic shut-off features to prevent overcharging. Always refer to the charger and battery manufacturer’s instructions. Overcharging may also reduce the battery’s capacity.
Troubleshooting Common Charging Problems
Even when you follow the instructions on how to connect charger clamps safely, issues might arise during the charging process. Troubleshooting means recognizing and fixing problems as they appear. It’s about knowing what to do if the charger doesn’t start, the battery doesn’t charge, or unusual things happen. This knowledge helps maintain the charging process.
Charger Doesn’t Turn On
If the charger doesn’t turn on, start by checking the power source. Ensure the charger is properly plugged into a working outlet. Check the circuit breaker to make sure it hasn’t tripped. If the power source is working, then there could be an internal issue with the charger. Inspect the charger’s fuse. Many chargers have a fuse that blows if there’s a problem.
- Check the Power Source: Make sure the charger is plugged in and the outlet is working.
- Examine the Fuse:
- Inspect the Charger Cable: Check the cable for any damage.
- Consult the User Manual: Refer to the charger’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
A tripped circuit breaker is a common cause if the charger isn’t powering up. This usually means the charger has drawn too much current, protecting the electrical circuit. If the circuit breaker frequently trips, this could indicate a problem with the charger or the electrical system. A blown fuse often safeguards the charger from internal damage. Fuses are designed to blow when excessive current flows through them. If the charger is relatively new and still doesn’t power on, there could be a manufacturing defect.
Battery Won’t Charge
A battery that won’t charge can be frustrating. Begin by re-examining the clamp connections. Double-check that they are connected correctly to the appropriate terminals. Make sure the clamps have a solid grip on the battery terminals. A weak connection can prevent charging. The battery might be too discharged to accept a charge, particularly if it has been deeply drained. Some chargers have a “desulphation” mode, which can sometimes revive deeply discharged batteries. If the battery is old or damaged, it might be unable to hold a charge.
- Check the Clamp Connections: Ensure the clamps have a secure grip on the terminals.
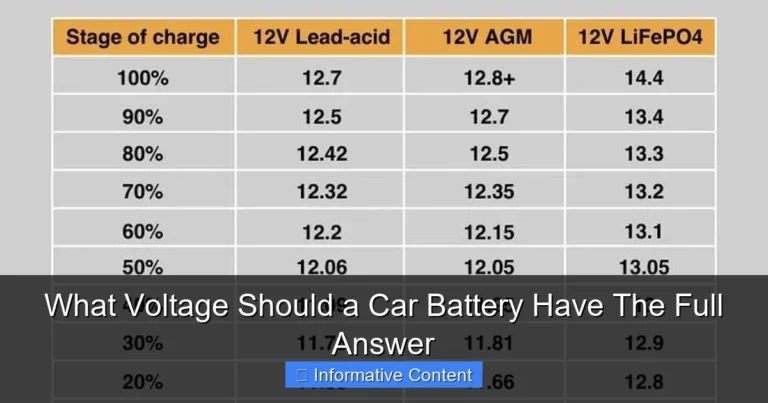
- Test the Battery: Consider using a voltmeter to verify the battery’s voltage.
- Inspect the Battery: Look for any signs of physical damage.
- Try a Different Charger: If possible, use another charger to see if it works.
Battery sulfation occurs when lead sulfate crystals build up on the battery plates. This build-up prevents the battery from accepting and holding a charge. Deep discharge can worsen sulfation. Old batteries will naturally lose their ability to hold a charge over time. Another possible issue is internal damage within the battery. The battery’s internal components may have worn out. A voltmeter can help to assess if the battery has a charge.
Other Unusual Issues
During the charging, you might spot some unusual happenings. Observe the battery’s condition throughout the process. A battery that gets very hot during charging is a sign of internal damage or overcharging. A battery leaking acid should be handled with extreme care. Always disconnect the charger immediately if you notice smoke, sparks, or a burning smell. These are clear signs of an electrical fault that needs attention.
- Battery Gets Hot: Disconnect the charger and check for issues.
- Battery Leaks: Handle with care and seek professional assistance.
- Smoke or Sparks: Immediately disconnect the charger.
- Charging Too Fast: Verify the charger settings and the battery’s capacity.
Overheating can lead to the battery’s internal components melting or even exploding. A battery leak indicates a breakdown of the battery’s structure. Battery acid can cause serious chemical burns. Smoke and sparks are signs of a short circuit or other electrical fault. A burning smell indicates that some components are overheating or melting. Always err on the side of caution. For any concerns, seek professional help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Can I charge a battery without disconnecting it from the car?
Answer: Yes, you usually can. Connect the charger clamps as described. However, some car manufacturers recommend disconnecting the battery or using a charger with a “battery reconditioning mode” to protect the car’s electronics.
Question: What’s the right charging time for a car battery?
Answer: The charging time depends on the battery’s size and the charger’s output. A slow, consistent charge is often best. Most chargers have settings or indicators that show the charging progress. Typically, it takes several hours to fully charge a car battery.
Question: Can I use a car battery charger on a motorcycle battery?
Answer: It depends on the charger. The charger should have a setting for smaller batteries or motorcycles to deliver a lower charging current. Using a charger with too high an amperage can damage a motorcycle battery.
Question: What should I do if the charger clamps spark when I connect them?
Answer: Disconnect the clamps immediately. There might be a short circuit or the connections are incorrect. Inspect the connections, and double-check the polarity. If the sparking continues, there could be a more serious electrical issue.
Question: Is it safe to leave the battery charger connected overnight?
Answer: It depends on the charger. Some smart chargers have automatic shut-off features that prevent overcharging, making them safe to leave connected. However, it’s always best to follow the charger’s instructions and monitor the charging process if possible.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how to connect charger clamps safely is a basic but important skill. You now have a clear guide on the critical steps. This involves preparing the work area, properly identifying and connecting the positive and negative terminals, and monitoring the charging process to prevent issues. Always remember that safety is the top priority. Correct polarity is crucial, and paying attention to signs like excessive heat or unusual smells is important. By following this guide, you can be sure of a safe charging experience for your car battery. Always prioritize safety. Charge confidently and take care of your vehicle.